善用擴增實境和虛擬實境科技促進教學效能
擴增實境和虛擬實境科技於職業專才教育的應用 職業專才教育着重培訓學生掌握真實工作環境所需的實際技能。學生須同時具備有關的知識與技能,以應付實際工作環境所面對的問題,設想解決辦法。千禧世代自小跟數碼科技結下不解緣,早已習慣這個學習環境,傳統上課模式已不能切合他們的需要了。擴增實境和虛擬實境等科技的面世不但帶動「數位原生代」(digital natives) (Prensky, 2001) 投入學習,促進教學效能;還幫助學生在安全的情況下,體驗實際工作時不同的情況及潛在的風險 (Reis, 2014) 。這些新科技配合適當的教材設計及教學設計,為21世紀打造一隊準備就緒及發展多元化的生力軍。 於職業訓練局實行「科技增潤學習」計劃 「科技增潤學習」是職業訓練局三年策略計劃(2016-2019)的發展項目之一。應用擴增實境和虛擬實境等科技,有助提升教學效能,引起學習興趣,幫助學生主動學習,促進師生彼此協作。怎樣能善用擴增實境和虛擬實境等科技,組織出色的課堂呢?以下例子提供了最好的答案。 青年學院(九龍灣)試用虛擬實境學習系統 去年十一月,青年學院(九龍灣)首度試用新落成的虛擬實境學習系統(Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training System, 簡稱VRSTS),並以「屋宇裝備工程」為首個培訓發展項目。此系統共分三部份:導師操作系統(Instructor Console)、虛擬實境圖像生產器(VR Graphics Generator)及模擬學習流動應用程式(Simulation App)。
 虛擬實境學習系統(Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training System, 簡稱VRSTS)。
(相片由Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project提供,2016)
虛擬實境學習系統(Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training System, 簡稱VRSTS)。
(相片由Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project提供,2016)
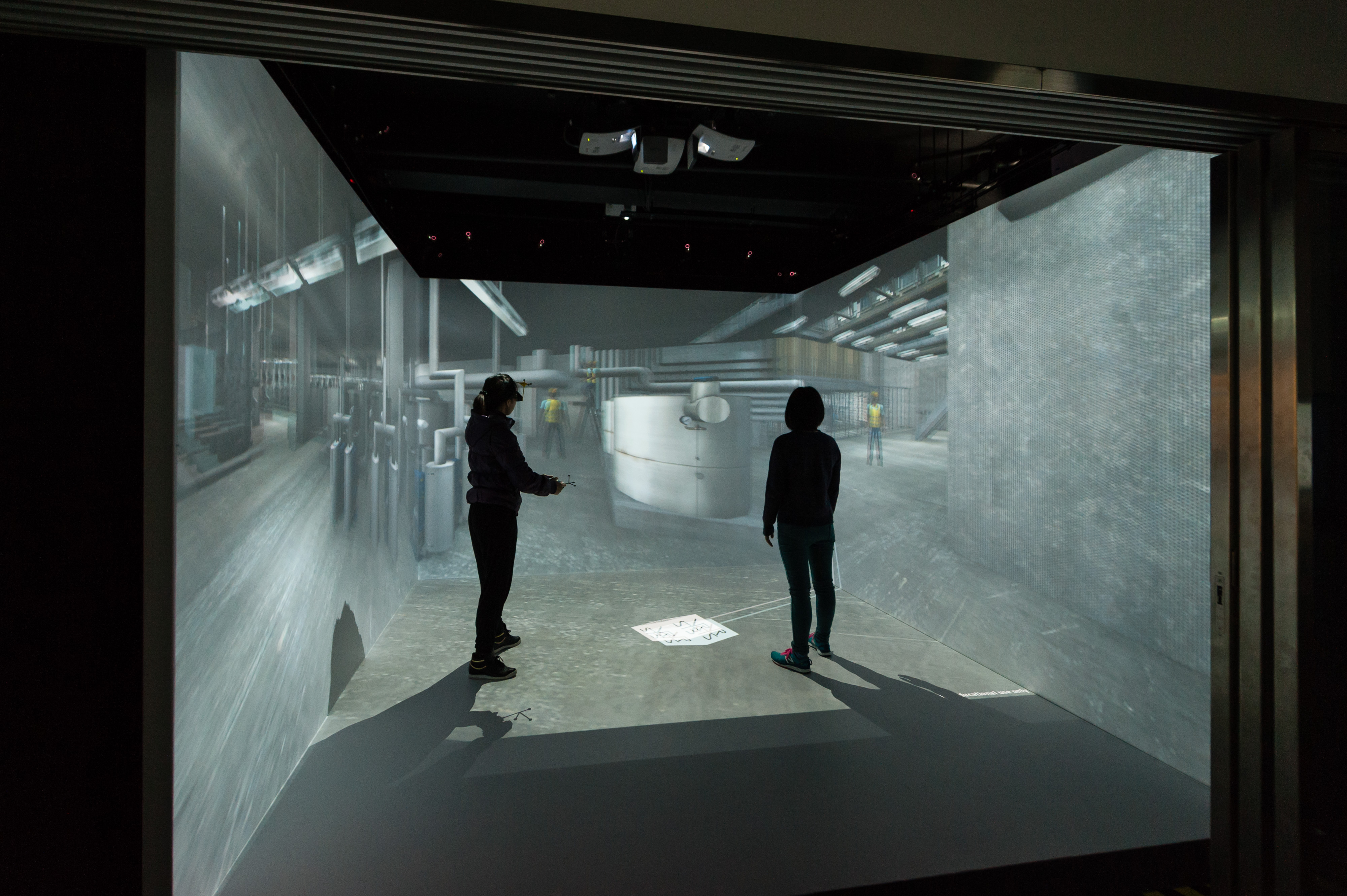 擴增實境/虛擬實境展覽室(AR/VR Showcase)為學生提供感官體驗。
(相片由香港專業教育學院(青衣)巿場推廣組提供,2016)
擴增實境/虛擬實境展覽室(AR/VR Showcase)為學生提供感官體驗。
(相片由香港專業教育學院(青衣)巿場推廣組提供,2016)

 上述兩圖是Browser內「空氣壓縮機」的快照。
學生可在此應用程式內自由旋轉立體模型,看到機器的正面圖及背面圖。
(相片由Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project提供,2016)
上述兩圖是Browser內「空氣壓縮機」的快照。
學生可在此應用程式內自由旋轉立體模型,看到機器的正面圖及背面圖。
(相片由Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project提供,2016)
 學生可按「壓縮機」、「儲氣缸」或「壓力錶」等圖標,看到指定機械組件的放大圖示。
(相片由Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project提供,2016)
學生可按「壓縮機」、「儲氣缸」或「壓力錶」等圖標,看到指定機械組件的放大圖示。
(相片由Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project提供,2016)
Enhancing Learning and Teaching with Augmented Reality (AR)/Virtual Reality (VR) Technologies
Application of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) in Vocational Education Vocational and Professional Education and Training (VPET) stresses on the mastery of hands-on skills and practices in authentic workplace. Learners have to acquire both knowledge and skills simultaneously before they are able to find a way out to tackle with problems experienced in real workplace. What complicates the matter is that the Millennials who grow up with the digital technology are more apt to think and learn in a media-rich learning environment. Dissemination of knowledge in the traditional classroom can no longer serve the purpose. The advances of Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) not only help to facilitate learning and teaching by engaging the “digital natives” (Prensky, 2001) in lessons, but also open up a new pathway to “expose the trainees to real-life (and potentially dangerous) situations with minimal risk” (Reis, 2014). Complemented with instructional design of learning materials and pedagogies, the cutting edge technologies are producing a cadre of work-ready graduates with diverse career opportunities for the 21st century. Implementation of Technology Enhanced Learning (TEL) in VTC According to the VTC’s 3-Year Strategic Plan 2016 to 2019, one of the initiatives is the development of Technology Enhanced Learning (TEL) in education. The application of AR and VR technologies opens up a new possibility to enhance learning and teaching for it can arouse learning interests, motivate students to be active learners and promote collaboration between teachers and students. How can we make good use of AR and VR technologies to deliver an engaging lesson then? An illustration of a telling example will be able to address this question. The Launch of Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training System (VRSTS) in the Youth College (Kowloon Bay) Last year in November, a Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training System (VRSTS) was first launched in the Youth College (Kowloon Bay) with Building Services Engineering as its pioneering target of practical training area. The system design consists of three components, namely, Instructor Console, VR Graphics Generator and Simulation App.
 The 3-tier system design of Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training System (VRSTS).
(Image Courtesy of the Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project, 2016)
The 3-tier system design of Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training System (VRSTS).
(Image Courtesy of the Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project, 2016)
 The AR/VR Showcase offers a sensory experience to learners.
(Image Courtesy of the Marketing Team, Hong Kong Institute of Vocational Education (Tsing Yi), 2016)
The AR/VR Showcase offers a sensory experience to learners.
(Image Courtesy of the Marketing Team, Hong Kong Institute of Vocational Education (Tsing Yi), 2016)
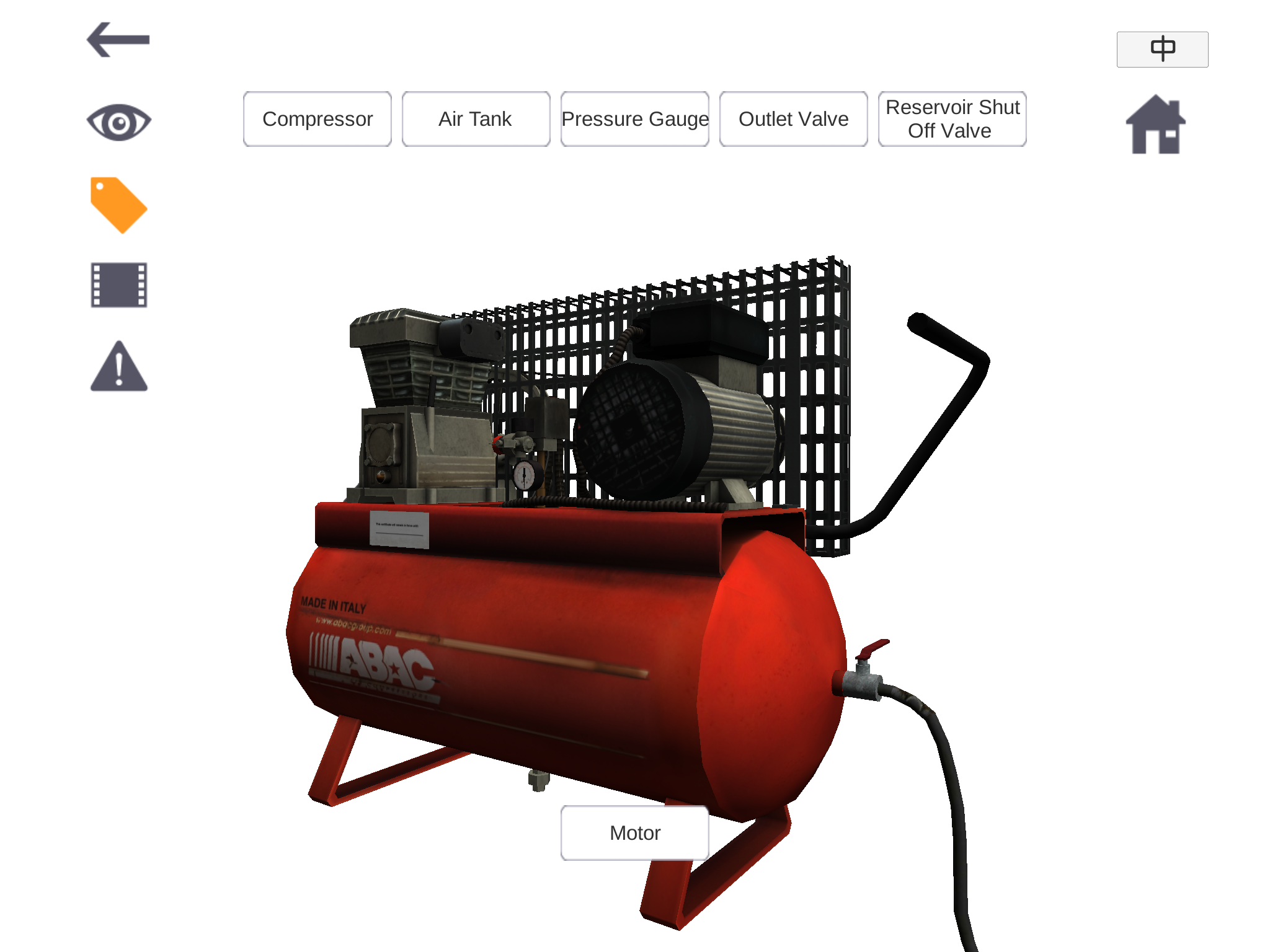
 The above pictures are snapshots of an air compressor in the Browser.
Students can rotate the 3D model with fingertips to see the front and back views of the machine.
(Image Courtesy of the Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project, 2016)
The above pictures are snapshots of an air compressor in the Browser.
Students can rotate the 3D model with fingertips to see the front and back views of the machine.
(Image Courtesy of the Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project, 2016)
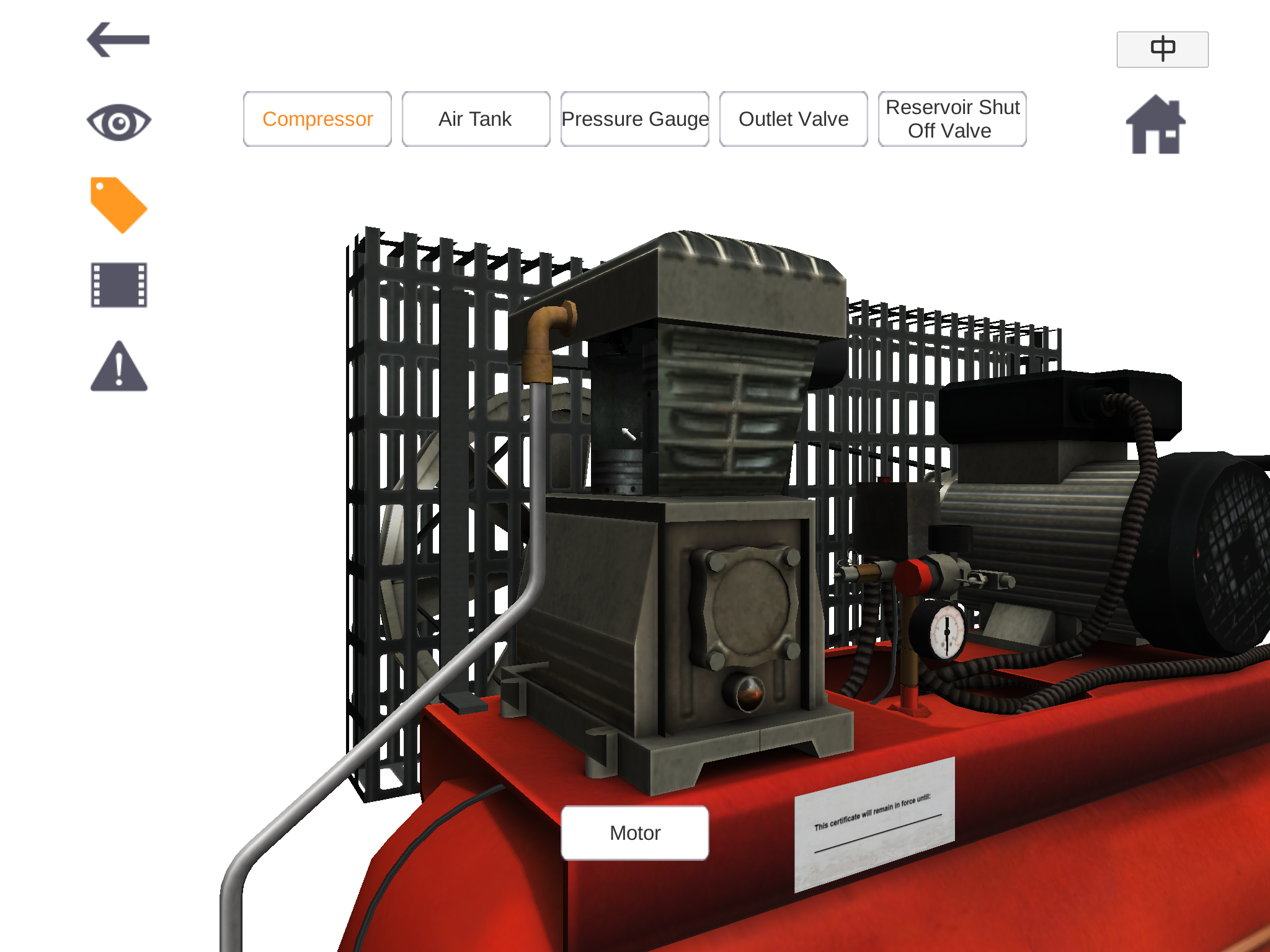 Students can also press such icons as “Compressor”, “Air Tank” and “Pressure Gauge” to view a particular part
of the machine in greater detail. All the terms of machinery parts are also available in Chinese version.
(Image Courtesy of the Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project, 2016)
Students can also press such icons as “Compressor”, “Air Tank” and “Pressure Gauge” to view a particular part
of the machine in greater detail. All the terms of machinery parts are also available in Chinese version.
(Image Courtesy of the Virtual Reality-based Simulation Training Project, 2016)
